
In cases like this, Tableau maps certain collations to others to minimize interpreting values incorrectly.
However, when you work with cross-database joins, you might join columns that have different collations.įor example, suppose your cross-database join used a join key comprised of a case-sensitive column from SQL Server and a case-insensitive column from Oracle. Usually, the collation is handled by the database. Working with multi-connection data sources is just like working with any other data source, with a few caveats, discussed in this section.Ĭollation refers to the rules of a database that determine how string values should be compared and sorted. Inspect the join clause to make sure it reflects how you want to connect the tables.Ībout working with multi-connection data sources Add one or more join clauses by selecting a field from one data source, a join operator, and a field from the added table.If Tableau uses Hyper to perform the join, this process happens in the background and no indicator is shown to identify where the join was performed. For instance, Tableau always chooses Hyper for non-inner joins. This behavior is pre-determined by a set of criteria including join types. Important: If you select Use Tableau or existing databases, Tableau chooses the fastest option when performing the join. The Cross-database join option changes from the default option, Using Tableau (using Hyper), to the new option Using your database, depending on what you choose. This option is the default and always uses Hyper to perform the join. This option allows Tableau to choose the fastest option to perform the join - either Hyper or the database you're connected to. In the Cross-Database Join dialog, select one of the following options, then click OK:.To change how Tableau performs the join, next to the Cross-database join option, click Edit.Otherwise, the Site Administrator may have set the Cross-Database Joins configuration option to Tableau only. Note: If you don't see this option, check that you're using only supported data sources and that you have only two data sources (one file and one database type). The Cross-database join option is displayed.
In the left pane, under Connections, click the Add button ( in web authoring) to add your second connection to the Tableau data source. Select the file or database that you want to connect to, then double-click or drag a table to the canvas.This step creates the first connection in the Tableau data source. In web authoring: From the Home or Explore page, click Create> Workbook to start a new workbook and then connect to your data.In Tableau Desktop: On the Start page, under Connect, connect to a supported file type or supported database type.Tableau Server: Enter the tsm configuration command tsm configuration set -k native_api.force_alternative_federation_engine -v trueįor more information about setting configuration values in Tableau Server, see tsm configuration set Options (Link opens in a new window) in the Tableau Server help.Įnable the performance option for cross-database joins.Tableau Desktop: Enter the command tableau.exe -DForceAlternativeFederationEngine=true.To enable this option enter the following information from the command line: The single database connection requirement still applies.
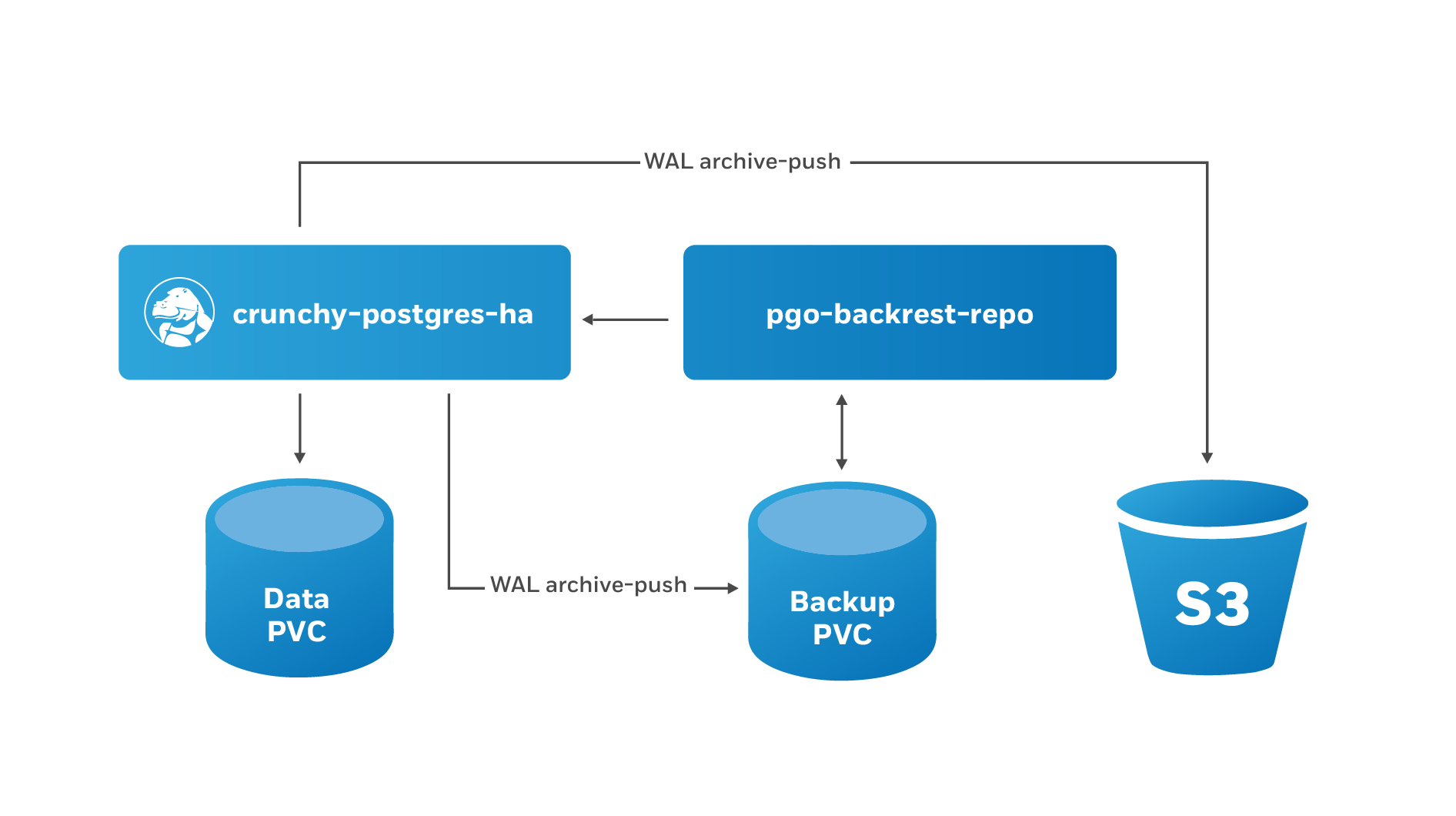
This enables you to experiment and determine optimal performance configurations.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
